利用MatDEM分析含瓦斯煤三轴压缩过程-中国矿业大学
论文题目
研究内容
In order to study the meso-mechanism of deformation,crack evolution, and energy conversion of gas-containing coal under loads,considering the gas pressure and adsorption expansion, the gas-solid coupling calculation program of MatDEM software was developed, and the triaxial compression process of gas-containing coal under different gas pressures was numerically simulated.
The results show that the strength and stiffness of gas-containing coal decrease with the increase of gas pressure. During the loading process, the permeability of the coal sample decreases first and then increases, while the initial permeability, minimum permeability, and maximum permeability all decrease with the increase of gas pressure. There are far more shear cracks in coal samples than tension cracks, and the number of cracks increases simultaneously with the peak stress drop.
With the increase of gas pressure, the macroscopic cracks in coal samples gradually change from large-angle shear cracks to multiple intersecting small-angle ones, and the coal sample gradually changes from brittle failure to ductile. There is an initial accumulation of elastic energy inside the gas-bearing coal, and the dissipated damping heat presents a stage change. As the loading stress level increases,the gas pressure gradually produces a degrading effect. The rockburst tendency of gas-bearing coal changes from weak to none with the increase of gas pressure, which is related to the evolution of the accumulated elastic energy and dissipated damping energy in the coal.

Figure 1: Numerical model of gas-containing coal sample and triangulation network.

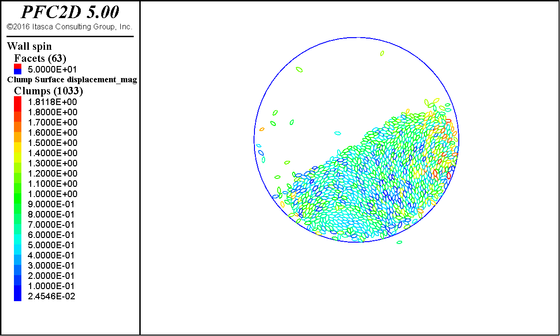
Figure 8: Axial stress distribution of particles under different stress levels
in gas-containing coal.

Figure 9: Pore pressure distribution under different stress
levels in gas-containing coal.

Figure 10: Distribution and evolution of cracks in gas-containing coal
under different gas pressures.
了解详情
Zhang, Z.H., Niu, Y.X., Shao, X.J. et al. Characteristics of Stress, Crack Evolution,and Energy Conversion ofGas-Containing Coal
under Different Gas Pressures[J] Geofluids,2021(Article5578636).