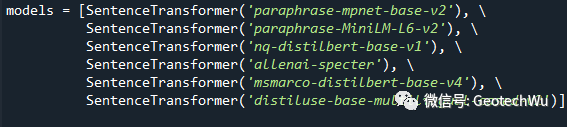
联合6种Transformers预训练模型
1 引言
在《SentenceTransformers库更新V2.0.0》中,我们引入了两种预训练模型:paraphrase-mpnet-base-v2和paraphrase-MiniLM-L6-v2。在此基础上又引入了4种预训练模型,包括Google和Bing的预训练模型,目前使用的模型如下图所示, 每种模型都取计算结果的Top 3。这个笔记仅报告了一个事实性的测试结果(factual report),对每个模型的计算效果未作评价。
2 测试
本次测试使用的句子为:"step-path jointed rock slope". 基于得出的18个记录,综合的测试结果如下:
[1] A DEM analysis of step-path failure in jointed rock(节理岩石阶梯式破坏的DEM分析)
[2] Challenges in the characterization of intact rock bridges in rock slopes(岩石边坡原岩岩桥特征分析面临的挑战)
[3] Rock Slope Stability Analysis by Using Integrated Approach(利用集成方法进行岩石边坡稳定性分析)
[4] Improvements to field and remote sensing methods for mapping discontinuity persistence and intact rock bridges in rock slopes.(改进现场和遥感方法,测绘岩石边坡不连续的贯通性和完整的岩桥)
[5] Rock mass structure characterisation---The development of a step-path failure surface is mainly controlled by the orientation and spatial characteristics of the present major rock structure including major joints sets, shear planes and fault planes. Step-path failure development requires a shallow dipping discontinuous major joint set crossed by a relatively steep discontinuous joint set in the rock mass (Ristau, 1994). The formation of a failure surface is impeded by the presence of intact rock bridges that may exist along shallow-dipping joint sets. A failure surface may be developed either by i) fracturing through the intact rock bridges in shear (Kemeny, 2005) through time dependent degradation of rock bridges or by tensile fracturing of closely spaced coplanar/parallel joints that are separated by a rock bridge, or ii) by by-passing the intact rock bridges if alternative cross joints are present that allow for a stepped failure surface which minimizes the effect of intact rock bridges on the slope stability.(岩体结构特征---阶梯式破坏面的发展主要受主要岩石结构的方向和空间特征控制,包括主要节理组、剪切面和断层面。阶梯式破坏的发展需要在岩体中出现一个浅倾不连续的主要节理组,与相对陡峭的不连续节理组交叉(Ristau,1994)。破坏面的形成受阻于沿浅倾角节理组可能存在的完整岩桥。破坏面可以通过以下方式形成:i)通过岩桥的时间退化,通过完整的岩桥断裂(Kemeny,2005),或者通过被岩桥分开的紧密间隔的共面/平行接头的拉伸断裂,或者ii)通过绕过完整的岩桥,如果存在替代交叉接头,可以形成阶梯式破坏面,使完整的岩桥对边坡稳定性的影响最小化。)
[6] Figure 2.12 shows a step-path failure in a coastal cliff in Australia which is formed by a combination of joint dilation of sub-vertical joints and failure of intact rock bridges located between the sub-horizontal, pre-existing discontinuities.(图2.12显示了澳大利亚沿海悬崖的阶梯式破坏,它是由次垂直节理扩张和位于次水平、预先存在的不连续体之间的完整岩桥破坏共同形成的。)
[8] The cave propagation behaviour of a jointed rock mass is strongly governed by the unique nature of joints and discontinuities, together with the intact strength of rock-bridges that make up a rock mass. (节理岩体的崩落传播行为在很大程度上受节理和不连续体的独特性质以及构成岩体岩桥的完整强度所制约。)
[8] The importance of intact rock bridges and step-path geometries in both engineered and natural rock slopes has been recognised for almost five decades; notwithstanding, reliable estimates of rock bridge percentages and the magnitude of rock bridge strengths to assume in slope analyses remains a major challenge.(近五十年来,人们已经认识到完整的岩桥和阶梯状的几何形状在工程和自然岩坡中的重要性;尽管如此,对岩桥百分比的可靠估计和在斜坡分析中假设的岩桥强度的大小仍然是一个重大挑战。)
[9] A step-path (or rock mass) failure occurs where toe break out and/or inter block shear develops through the combined sliding along non-persistent joints and failure of intact rock bridges.(阶梯路径(或岩体)破坏发生在坡脚断裂和/或块状物之间的剪切,通过沿贯通性节理的滑动和完整岩桥的破坏而形成。)
[10] Step-path analyses of rock slopes was first discussed in detail by Jennings (1970) who used a limit equilibrium approach that incorporated shear failure along joints, shear through intact rock and tensile failure of rock bridges. (Jennings(1970)首次详细讨论了岩石斜坡的阶梯式分析,他使用了一种极限平衡方法,其中包括沿节理的剪切破坏、通过完整岩石的剪切和岩桥的拉伸破坏。)